Everything You Need to Know About CBD
If you’re here, you probably have questions about CBD. What is it – and does it work? Our team regularly hears from customers who want to learn more about the natural compound that’s everywhere these days – from your favorite coffee shop to mall kiosks, you’ve likely seen claims about CBD that sound too good to be true. Let’s explore what CBD is, how it works, how to manufacture CBD and why it’s growing in popularity. Whether you’re new to CBD or have been taking it for years, this comprehensive guide gives a conclusive answer to all your CBD-related questions.
What is CBD?
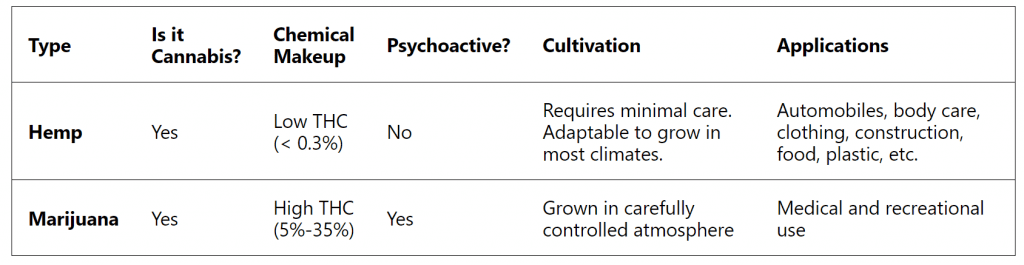
CBD, or Cannabidiol, is a chemical compound found in both Hemp and Marijuana plants. While the plants are both members of the Cannabis family, they differ significantly in composition. Hemp plants have less than 0.3 percent THC. In contrast, Marijuana has anywhere from 3 to 35 percent THC.
Hemp requires lower maintenance than Marijuana and is also cheaper in bulk. It has applications in body care, clothing, and construction. Most CBD companies use Hemp-derived CBD for two reasons: It’s more cost-effective and meets regulation standards. Federal and many state regulations are making the distinction between hemp-derived and marijuana-derived products due to the difference in THC concentrations. With CBD won’t get you “high” – even in its rawest form, Hemp isn’t associated with psychoactive effects.
CBD and THC are just two of the cannabinoids, or chemical compounds, found in Cannabis plants. Researchers have discovered dozens of other compounds. Some others that you may hear referenced when discussing CBD:
- Cannabichromene (CBC)
- Cannabidiol Acid (CBDA)
- Cannabidivarin (CBDV)
- Cannabigerol (CBG)
- Cannabinol (CBN)
- Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV)
Where is CBD Sourced?
Now that you know more about Hemp-derived CBD, you may be wondering where Hemp comes from. The answer is more complicated than you may expect. For a long time, almost all CBD products came from European farms. That’s because growing Hemp was illegal in the U.S. – but one piece of legislation ended up changing the game. The Agricultural Act of 2014, or 2014 Farm Bill, made it legal to grow Hemp without having a permit from the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration – a significant milestone that helped CBD become mainstream.
Why was Hemp illegal? In 1971, The Controlled Substances Act made Cannabis a Schedule 1 substance. Per the DEA, a Schedule 1 substance is one that has “no currently accepted medical use in the United States, a lack of accepted safety for use under medical supervision, and a high potential for abuse.” More than 40 years later, the government acknowledged Hemp’s potential by making it legal to farm under research and pilot programs.
The 2018 Farm Bill further cemented Hemp’s legality in the U.S., as it explicitly makes Hemp legal in all 50 states and provides support for farmers who cultivate the plant. Hemp Bombs sources all its CBD from superior-grade Industrial Hemp grown in the U.S.
How is CBD Extracted?
There’s more than one way to bake a cake, and the same can be said for extracting CBD. Hemp Bombs extracts and manufactures our CBD using a specialized process that results in CBD containing less than 0.3% THC, making all our products federally legal.
CBD Intake
It’s important to know that we are not doctors and cannot provide exact CBD intake recommendations – you should take the amount that feels best for you. However, we can provide you with general guidelines and some basic information on the metabolization process to steer you in the right direction. CBD works with your body’s natural biochemistry and metabolism, and everyone reacts to CBD differently. A few of the things that may affect how you process CBD are diet, sex, weight and age.
The best approach is to begin with small servings and gradually increase your intake. This will better allow you to understand how your body processes the compound and help you find the amount that brings you the most comfort. Try your best to take CBD daily for desired effects and increase servings by a few milligrams if you don’t see your desired effects. It also depends on why you’re taking CBD - consider whether your discomfort is mild, severe or persistent, and decrease or increase your serving accordingly. See our CBD intake guide.
How Does CBD Interact with Your Body?
CBD is effective because of the Endocannabinoid System, or ECS, a biological system found in mammals. It is a collection of cell receptors and molecules spread throughout the body that affects mental clarity, appetite, sleep and more. Receptors are gatekeepers to different molecules and are activated by chemical molecules called agonists. When an agonist binds with a receptor, a message is passed on to the cell.
The two cell receptors involved in the Endocannabinoid System are called CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors are most commonly found in the brain and spinal cord, while CB2 is in the peripheral nervous system, central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract. Endocannabinoids are the chemical messengers that signal certain functions with the ECS network. The overarching purpose of the ECS is to maintain homeostasis (body balance).
Anandamide and 2-Arachidonoylglycerol, or 2-AG, are the two primary endocannabinoids active in the ECS. Anandamide has been dubbed the “bliss molecule” and plays a role in the regulation of appetite, pleasure and reward. 2-AG is thought to affect immune system functions and pain management.
One CBD misconception is that it binds directly to receptors CB1 and CB2 – in reality, Cannabidiol has a low binding affinity with those receptors. The effects of CBD occur because of an enzyme called FAAH (Fatty acid amide hydrolase). FAAH is responsible for breaking down anandamide, and CBD inhibits FAAH. The result is higher levels of anandamide, which means increased feelings of well-being.
We’ve covered some of the minor differences between CBD and THC, especially as it relates to intoxication. Let’s explore another difference between the two compounds. While both CBD and THC interact with the Endocannabinoid System, they affect your body in significantly different ways. THC binds with the CB1 receptor, but CBD can sometimes be an antagonist of THC. Essentially, it works against a THC “high,” which is why some people take CBD and THC together. Of course, one of the most significant differences is legality. THC is illegal in many states and can carry a hefty prison sentence and fines. In comparison, CBD is federally legal in all 50 states and many countries.
CBD in Review
When you look at CBD’s potential benefits, it’s no surprise that the industry is exploding. Forbes estimates that CBD will be worth $22 billion in 2022 – impressive for an industry that only began to gain traction in 2014. The future for CBD is bright.
With the market growing at such a rapid pace, hundreds of companies are throwing their hats in the ring. Because the FDA doesn’t regulate CBD, some companies claim to have pure CBD while selling a product filled with unnecessary additives and chemicals. That’s why it’s important to choose a trusted brand like Hemp Bombs. With third-party lab tests, reviews from real people and transparency about manufacturing, we set ourselves apart from the competition and provide you with the best products available. For additional information, be sure to check out our helpful CBD facts page that contains lots of useful information about CBD and its benefits. And for specific information about CBD Gummies, click here: What do CBD Gummies do?
SOURCES:
https://www.chronictherapy.com/hemp-oil-vs-cbd-oil-differences/
https://www.leafly.com/news/science-tech/cbd-vs-thc-cbd-not-intoxicating
https://www.leafscience.com/2017/11/22/thc-cbd-difference/
https://echoconnection.org/4-differences-cbd-thc/
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/cbd-oil-benefits
https://medium.com/@mary_c_biles/anandamide-the-bodys-own-antidepressant-and-how-to-boost-it-naturally-895cdafcf7fe
https://sensiseeds.com/en/blog/cannabinoid-science-101-what-is-2-arachidonoylglycerol-2-ag/
https://sensiseeds.com/en/blog/cannabinoid-science-101-what-is-anandamide-aea/
https://www.leafscience.com/2017/03/17/the-endocannabinoid-system-a-beginners-guide/
https://herb.co/learn/what-is-the-endocannabinoid-system/
https://medium.com/@mary_c_biles/anandamide-the-bodys-own-antidepressant-and-how-to-boost-it-naturally-895cdafcf7fe
https://www.leafly.com/news/science-tech/the-endocannabinoid-system-and-cbds-role-in-stress-anxiety-and-fe
https://wayofleaf.com/cbd/101/cbd-oil-dosage
https://ministryofhemp.com/different-types-cbd-oil/
https://hightimes.com/guides/what-are-terpenes/
https://hightimes.com/sponsored/top-5-ways-to-take-cbd-finding-the-right-product-for-you/
https://www.leafly.com/learn/consume/edibles/what-is-decarboxylation
https://wayofleaf.com/cannabis/101/cbd-cannabis-extraction
https://ministryofhemp.com/europe-hemp-cbd/
https://madebyhemp.com/what-is-industrial-hemp-where-does-it-come-from/
https://www.leafly.com/news/cannabis-101/what-is-cannabinoid
https://ministryofhemp.com/hemp/not-marijuana/
https://projectcbd.org/what-is-cbd/
https://hightimes.com/health/cannabidiol-cbd/